



Technologies - Gasification
Low-Pressure Gasification
The Vermont Gasifier operates at low pressure, has a high throughput, and produces a medium-Btu gas that can directly fuel a standard, unmodified gas turbine.
DOE is currently co-sponsoring a scale-up demonstration of a low-pressure gasifier in Burlington, Vermont.
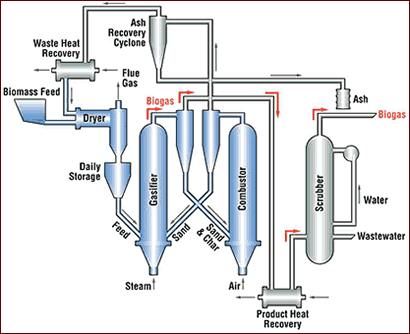
The
gasifier at McNiel Station in Burlington, VT operates at low pressure, has
a high throughput, and
produces a medium-Btu gas that can directly fuel a standard, unmodified
gas turbine.
This process uses two reactors where two separate chemical reactions take place. In the first reactor, biomass is surrounded by hot sand where pyrolysis takes place and the volatile chemical components of biomass separate from the remaining solids consisting of char, ash, and the sand. The gases are separated from the solids in a cyclone separator, and the sand and char move on to the second reactor. There the char is burned to provide heat for the pyrolysis and gasification in the first reactor.
The gas passes through a scrubber to remove particulate matter to meet the particulate specifications of a gas turbine. The resulting gas has a medium-Btu content of about 500 Btu per cubic feet and is suitable for fueling a standard gas turbine.